General concepts in public systems
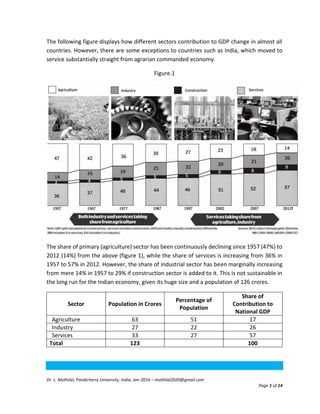
- 1. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 1 of 14 The following figure displays how different sectors contribution to GDP change in almost all countries. However, there are some exceptions to countries such as India, which moved to service substantially straight from agrarian commanded economy. Figure.1 The share of primary (agriculture) sector has been continuously declining since 1957 (47%) to 2012 (14%) from the above (figure 1), while the share of services is increasing from 36% in 1957 to 57% in 2012. However, the share of industrial sector has been marginally increasing from mere 14% in 1957 to 29% if construction sector is added to it. This is not sustainable in the long run for the Indian economy, given its huge size and a population of 126 crores. Sector Population in Crores Percentage of Population Share of Contribution to National GDP Agriculture 63 51 17 Industry 27 22 26 Services 33 27 57 Total 123 100
- 2. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 2 of 14 Overview: Management of Various Public Systems a) Central Administration Parliament (consists of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha) Judiciary b) State Administration Units Municipal Corporation Municipality District (Zilla Parishad) Taluks / Mandal / Tehsil Village c) Statutory Autonomous Bodies UPSC Election Commission SEBI d) Public Sector Enterprises Townships Cantonment Areas Economic Systems & Development Models: 1. Capitalism Private property Market based – supply – demand Earnings (income) according to ability Maximum individual freedom Promotes competition 2. Socialism Karl Marx advocated Socialization of all means of production Central planning – state direction of economy Reward according to work done ( Ex: USSR, China, Vietnam, Cuba) Comprehensive state planning
- 3. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 3 of 14 Public ownership of means of production ( Land and Capital) Private property is permissible (Housing) 3. Communism Advanced form of Socialism Very Idealistic No private property Reward – need of everybody Complete Communism – embraces not only property but also wives and children (Plato) Production according to the needs Extreme communism – nowhere existed Object : Remove the ground for civil suits Promote harmony Unite all citizens by common interest Aristotle : Against Plato’s Communism More things in Common Common Meals 4. Mixed Economic System Capitalism + Socialism (Synergy) Prof. Pigou: Socialist central planning is good, if it could be efficiently organized and preferable to capitalist system Keynes: Capitalism helps to promote competition & leads to efficiency in production Compromise between High degree of state intervention and free enterprise capitalist economy Frame-work of mixed economy: Co-existence of private and public sector Positive economic role of the state : Serving community may be made condition to Private Sector Strategic and Industries of National importance in Public Sector Better distribution of ownership Architect of Indian planning, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru’s vision - “Democratic Socialism”
- 4. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 4 of 14 INDIA’S IDEOLOGY The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. It lays down the framework defining fundamental political principles, establishes the structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions, and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens. It is the longest written constitution of any sovereign country in the world (wikipedia.org, 2011) Philosophy of the constitution: India to be a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic, assuring its citizens of justice, equality, and liberty, and endeavours to promote fraternity among them. The words "socialist" and "secular" were added to the definition in 1976 by constitutional amendment. Democratic Republic = Source of authority – people (Government of the people, by the people and for the people) 26th January, 1950 – Constitution of India came into force
- 5. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 5 of 14 PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION Definitions 1. Prof. Woodrow Wilson: “Detailed and systematic execution of public law”. 2. Prof. Pfifner: “Public administration is the coordination of collective efforts to implement public policy”. 3. Waldo: “Public administration is the art and the science of management as applied to the affairs of state”. 4. Marshall E. Dimock: Administration is concerned with “what” and “how of government”. What: It is the subject matter, the technical knowledge of a field which enables an administrator to perform his/her task. How: It is the technique of management – a process through which programmes are carried out. Public administration is concerned with the conduct and management of public activities. It is systematic execution of the will of the people, which has been discovered, formulated and expressed in the form of laws by the legislature. It is to do with the people and not with things. Private Administration – Ex: Management of clubs, company, institutions, etc. Public Administration – Management of affairs of the public by central, state or local government or statutory bodies. Ex: Post offices, SEBI, RBI, SEBs. Scope of Public Administration – POSDCORB View: P – Planning: First step of public administration O – Organization: Establishment of formal structure of authority, through which the work is subdivided, arranged, defined and coordinated. S – Staffing: Recruitment and training and maintenance of work environment.
- 6. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 6 of 14 D – Directing: Continuous task of making decisions, issuing specific and general orders. CO – Coordination: Channelization of forces into an integrated flow to achieve the goals set up. R – Reporting: State of activities – stage of work. B – Budgeting: Accounting, fiscal planning and control (finance). The above points are not exhaustive as a criminal cannot be caught with the above procedure. Study of Public Administration includes all the process of Policy Formulation Political Parties & Public Opinion Relationship of Public Administration with: 1. Politics – Making Policy 2. Public Administration – Study of Human Action & Implementation of Policy 3. Economics – Budgeting, Management of Government Cost. 4. Psychology – Study of Human Behavior Principles of Public Administration: 1. Political Direction and Political Executive 2. Public Responsibility – acts can be questioned any time, therefore, records must be preserved. 3. Social Necessity 4. Efficiency 5. Organization 6. Public Relations 7. Research Methods applied to study Public Administration: 1. Experimental Method – every new policy 2. Historical Method – attempts to study past and analyses the situation 3. Case Method – particular case is analyzed 4. Psychological Method 5. Quantitative Method
- 7. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 7 of 14 CIVIL SERVICES Position of civil servants in a parliamentary system of government. Political Executive – Policy is Laid Down Permanent / Technical Executive (possesses expert knowledge of administration) - Policy is carried out and Administration is run. Joint select committee on Indian Constitutional Reforms: “The system of representative government to be successful in practical working requires the existence of competent and independent civil servants capable of giving advice to successive ministers”. Democratic System into Bureaucracy Proper Solution: Select right type of men & women – efficient and honest and can be trusted with confidence. Conditions of Services: Constitution does not have detailed guidelines. But by the acts of appropriate legislatures. Public Service Commission – for each state and Union Territory. Members of Public Service Commission are appointed by: President (Central Government) for Union / Joint commission Governor (State government) for State Commission Functions of Public Service Commission – assigned by the government. Report of Public Service Commission: Central Govt.– President – laid down before parliament ( both houses ) State – Governor – laid down before legislature Commissions Advice – only Advisory, Not Obligatory Max Weber (1864-1920), known as the Father of Modern Sociology, analyzed bureaucracy as the most logical and rational structure for large organizations. Bureaucracies are founded on legal or rational authority which is based on law, procedures, rules, and so on. Positional authority of a superior over a subordinate stems from legal authority. Charismatic authority stems from the personal qualities of an individual. Efficiency in bureaucracies comes from: (1.) clearly defined and specialized functions; (2.) use of legal authority; (3.) hierarchical form; (4.) written rules and procedures; (5.) technically trained bureaucrats; (6.) appointment to positions based on technical expertise; (7.) promotions based on competence; (8.) clearly defined career paths. (Wikipedia)
- 8. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 8 of 14 Civil Services in India 1. All India Services I.A.S ( UPSC ) I.P.S ( UPSC ) Indian Forest Service ( UPSC ) 2. Central Services including Indian Foreign and Revenue Group – A & B ( UPSC ): 2+45 Services Group – C & D ( Selection through SSC – Non-Gazetted ) 3. State Administrative Services – Individual States Civil Services Training 1. Generalist – Regulatory and Developmental ( Policy Formulation and Implementation ) 2. Specialist: Technical Engineering Medical Agriculture Professional Taxation Education Judiciary Statistics Accounts Training Institutes ( with functional specialization ) at four levels 1. National 2. Regional 3. State 4. Local Management of Training Institutes by: 1. Central Government 2. Autonomous 3. State Government
- 9. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 9 of 14 1. Central Government: Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration at Mussoorie (Foundation training) Institute of Secretariat Training and Management, New Delhi (In- service and Refresher Training Program) 2. Autonomous: IIMs Administrative Staff College, Hyderabad Institute of Social and Economic Change at Bangalore IIPA, New Delhi ( only Govt.) – Research and Consultancy Services Other Public Sector Undertakings – BHEL, LIC, AIR INDIA have their own training wings. 3. States States differ in training Training Policy in India does not have integrative approach Training Policy is needed with vision, mission & clear contents. Need to Development of Professionalized Training Faculty for the Clerical Staff is almost neglected STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT DEPARTMENTS Number of Ministries – Single/No. of Departments Each Ministry is headed by Political Chief Executive – Minister. Minister is assisted by: Minister of State Deputy Minister The head of the Secretariat Organization of Department/Ministry is Secretary (Member of Indian Civil Service) Secretary staff consists of 2 categories of personnel Officer Class ( has 4 regular grade ) Subordinate Class
- 10. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 10 of 14 SECRETARY (In charge of Department) JOINT or ADDITIONAL SECRETARY (In charge of a wing consisting usually 8 sections) DEPUTY SECRETARY (4 sections) UNDER SECRETARY (In charge of branch with 2 sections) ASSISTANT SECRETARY SECTION SUPERINTENDENT (In charge of 1. Section) ASSISTED BY CLERICAL STAFF i. UDC/ASSISTANTS ( can be promoted through competitive exam/promotion) ii. LDC ( can be promoted through competitive exam ) Besides Secretariat, there are number of attached offices. Ex. UPSC, Election Commission, etc. Attached offices functions are specific/advisory & their status is lower than Secretariat.
- 11. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 11 of 14 “BUREAU” & “BOARD” TYPE OF ORGANIZATIONS 1. Bureau – Responsibility is vested in one person. Ex. CBI 2. Board/ Commission – Responsibility is vested in several individuals. Ex. UPSC, SPSC, University. Advantages: A. Bureau Type : Quick decisions Unity of purpose (Responsibility) Policies are well executed Clearly defined and easily located Economical Motivation, work with greater zeal, energy and devotion – because responsibility is known B. Board Type : Where policy and technique to be followed are not fully settled and discussion is necessary Conflict interests of 2 or more parties have to be adjusted Avoid party politics and give equal representation Save from external pressures. Ex. UPSC members
- 12. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 12 of 14 Current Developments in PSM 1) Deregulation - To reduce the amount of regulation over a market or economy. It may include reduced or eliminated requirements for reporting or filing statements with regulators. Deregulating may allow an organization to conduct more activities than it could before; for example, it may allow a bank to make more high risk investments. Deregulation is intended to increase efficiency in the market by letting the Invisible Hand guide the economy apart from government intervention. Opponents, however, argue that deregulation increases the likelihood of fraud and unfair practices such as insider trading. Many analysts agree that deregulation helps firms on solid financial footing and hurts those that are not (http://financial- dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/deregulation, 2013). 2) Privatization- Def: Privatization/denationalization or disinvestment is the transfer of partial or complete property or responsibility from the public sector (government) to the private sector. A similar transfer from the private sector to the government is called the nationalization or municipalization of some property or responsibility. Types of Privatization: There are mainly three methods of privatization: I. Share Issue privatization (SIP) - selling shares on the stock market (most common type) Share issue can broaden and deepen domestic capital markets, boosting liquidity and potentially economic growth, but if the capital markets are insufficiently developed it may be difficult to find enough buyers, and transaction costs (eg underpricing required) may be higher. For this reason, many some governments elect for listings in the more developed and liquid markets such as Euronext, the London, New York or Hong Kong Stock Exchanges which are popular because they are highly developed and sophisticated (Wikipedia) II. Asset Sale privatization - selling the entire firm or part of it to a strategic investor, usually by auction. III. Voucher privatization - shares of ownership are distributed to all citizens, usually for free or at a very low price. Because of higher political and currency risk deterring foreign investors, asset sales are more common in developing countries.
- 13. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 13 of 14 Voucher privatization has mainly been used in the transition economies of Central and Eastern Europe - countries such as Russia, Poland and Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic and Slovakia) – (Wikipedia) A very substantial benefit to share or asset sale privatizations is that bidders compete to offer the state the highest price, creating revenues for the state to redistribute in addition to new tax revenue (Wikipedia). Voucher privatisations, on the other hand, would be a genuine return of the assets into the hands of the general population, and create a real sense of participation and inclusion. Vouchers, like all other private property, could then be sold on if preferred (Wikipedia). Reasons for Privatization: Performance. Government-run industries tend to be bureaucratic. A political government may only be motivated to improve a function when its poor performance becomes political issue, and such an improvement is easily reversed by another regime. Improvements. The government may put off improvements due to political sensitivity and special interests. Corruption. Decisions are made primarily for political reasons, personal gain of the decision-maker (i.e. “graft”), rather than economic ones. Accountability. There is no accountability for misdeeds and violations of the provisions of the law. Punishments are very meager for wrongdoers. Goals. A political government tends to run an industry or company for political goals rather than economic ones. Capital. State-owned industries have to compete with demands from other government departments and special interests. Security. Governments have had the tendency to “bail out” poorly run businesses, often due to the sensitivity of job losses. Lack of market discipline. Poorly managed state companies are insulated from the same discipline as private companies, which could go bankrupt, have their management removed, or be taken over by competitors. Natural monopolies. The existence of natural monopolies does not mean that these sectors must be state owned. Governments can enact or are armed with
- 14. Dr. L. Mothilal, Pondicherry University, India, Jan-2016 – mothilal2020@gmail.com Page 14 of 14 anti-trust legislation and bodies to deal with anti-competitive behaviour of all companies public or private. Political influence. Nationalized industries are prone to interference from politicians for political or populist reasons. 3) Global Trends: All over the world there has been change in public systems. They have been reoriented with reality. They are also using modern tools and techniques of management. Privatization programmes have been undertaken in many countries across the world, falling into three major groups (Wikipedia). The first is privatization programmes conducted by transition economies in Central and Eastern Europe after 1989 in the process of instituting a market economy. The second is privatization programmes carried out in developing countries under the influence of international financial institutions such as the World Bank and IMF. The third is privatization programmes carried out by developed country governments, the most comprehensive probably being those of New Zealand and the United Kingdom in the 1980s and 1990s. 4) Approaches to Productivity in Public Systems Management: a. Usage of Technology – Computers b. Simple Automation c. Workflow Management d. E-governance e. Ethical issues: Conception, Design, Execution of Project, and Review of Systems References: 1. Wikipedia.org 2. http://financial-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/deregulation
