Macromolecules Chemistry Life
- 2. The Chemistry of Life Our first topic Macromolecules focuses on the Chemistry of Life You are made up of chemical elements and their compounds or mixtures. The basic elements of life are listed on the Periodic Table.
- 3. Topic 1: Macro molecules To be able to understand Biology we must ensure that we can read, pronounce, spell, write and interpret the language used. What does ‘macro’ mean? What is the definition for the term ‘molecule’?
- 4. Macro = BIG OR LARGE A MOLECULE is made up of two or more atoms chemically combined in a fixed ratio to form the smallest particle of a substance which can exist by itself.
- 5. Molecules Molecules may be represented by chemical formulae eg H20 The formula represents what atoms combine chemically to form the smallest possible particle of water. So one molecule of water contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom
- 6. The language of Biology Page 19 Biology The Essentials workbook Check out the list of terms given in Q1. Could you explain what ……..each term means? ……..some of them mean? ………. any of them mean? In order to achieve successful learning outcomes you must be able to understand the language used and so must learn definitions as we go.
- 7. Macromolecules classification There are 4 major groups of these large complex organic molecules:
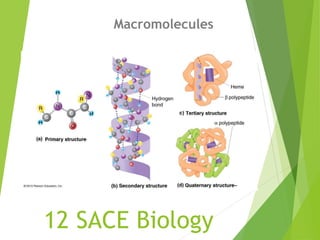
- 9. M6 Polymer Principles Four classes of macromolecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymers are made up of smaller parts called monomers. Polymers are formed through condensation reactions. Polymers are broken apart through a hydrolysis reaction.
- 10. General Information about Carbohydrates Are important energy sources for most organisms Often end in “-ose” Made of C, H, and O “Carbo”-contains carbon “Hydrate”-hydrogen and oxygen are present in the same proportions as in water (2 H: 1 O)
- 11. Carbohydrates Use the molecular model kits to construct a glucose model C
- 13. Simple or single sugars are monosaccharides Two linked monosaccharides are disaccharides Long chains of monosaccharides are polysaccharides
- 14. Monosaccharides -one sugar unit – are the simplest carbohydrates They have a backbone of 3-7 carbon atoms There are many –OH and –H functional groups present They are usually found in ring form in cells They are characterized by sweet taste They have several polar -OH groups, so they dissolve in water
- 15. GLUCOSE (C6H12O6) This is the most common monosaccharide It is one of the products of photosynthesis. In animals, glucose is synthesized in the liver and kidneys Glucose is needed for ATP synthesis during cellular respiration
- 16. Glucose and fructose have the same chemical formula C6H12O6 but different structural arrangement of the atoms (called isomers)
- 18. FRUCTOSE Fructose is found in fruits and honey. It is classified as the sweetest of all the sugars.
- 19. Ribose and deoxyribose are the building blocks for nucleic acids.
- 20. Disaccharides – these are two sugar units bonded together formed in condensation reactions
- 22. Maltose (two glucose units) is present in germinating seeds.
- 23. Sucrose (glucose + fructose) is a transport form of sugar used by plants and harvested by humans for food.
- 24. Lactose (galactose and glucose) is present in milk
- 25. Polysaccharides Large molecular compound of hundreds (or thousands) of simple sugar units, monomers, (monosaccharide's) linked together. These include; Cellulose – major component that encloses plant cell cells. Tough and fibrous. Unable to be digested and broken down by most organisms including humans. Chitin – found in exoskeletons of organisms such as spiders, insects and crustaceans. Acts as support.
- 26. Starch and Glycogen Both are storage molecules for energy in living organisms. Plants- convert sugars into starch enables the plant to store excess as an energy source. Animals- excess glucose is stored in liver and muscles as glycogen. A gram of fat stores twice as much energy as a gram of polysaccharide.
- 27. Practical Testing for Starch Sugar(glucose) Protein Fats
- 28. 1.Used as structural component for membranes 2.Energy storage systems in organisms. 3.Protective components of cell walls 4.Insulation They are organic molecules composed of fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol backbone. These include the following; Lipids
- 29. Lipid Molecule
- 30. Fats and Oils- solid fat reserves stored as adipose tissue. Acts as a storage of energy and insulation against cold. Oils are mainly liquids and found in plants and act as reserves of energy. Steroids- Large lipids and have important roles as functional molecules e.g. cholesterol Waxes- produced by plants and animals. Act a protective layers.
- 31. Elements of life Back to pg 19 Essentials Q1 What do you think the difference between a lipid and a phospholipid would be? Song - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nt9u7Cf Voc4
- 32. Phospho lipids contain phosphorus The element phosphorus can be located on the Periodic Table Without phosphorus in the DNA we would not exist. Life depends on the chemical elements which form a wide variety of different chemical substances. Phospholipids- includes a phosphate group, so when in water arrange themselves in rows forming a double layer which in turn creates a boundary between the cell and it external environment.
- 37. Note key points Do focus questions on p22