Electrophoresis Separation Techniques
- 1. MANEESHA M JOSEPH MSC MLT (MICROBIOLOGY)
- 2. ELECTROPHORESIS It is the process of moving charged biomolecules in an electrolyte solution by applying an electrical field across the mixture. Biomolecules will move with a speed, dependent on their charge, shape, and size. separation occures on the basis of their molecular size. Electrophoresis is used: for analysis and purification of very large molecules (proteins, nucleic acids) for analysis of simpler charged molecules (sugars, amino acids, peptides, nucleotides, and simpler ions).
- 3. When charged molecules are placed in an electric field, they migrate toward either the positive (anode) or negative (cathode) pole according to their charge. Factors influenced electrophoresis mobility: 1.net charge of the molecule 2.size and shape 3.concentration of the molecule in solution SUPPORTING MEDIA Solid matrix with pores which are used: • paper • starch • cellulose acetate • polyacrylamide • agar/agarose Molecules in the sample move through porous matrix at different velocity.
- 4. BUFFERS Function of buffer 1. carries the applied current 2. established the pH 3. determine the electric charge on the solute High ionic strength of buffer produce sharper band produce more heat Commonly used buffer Barbitone buffer & Tris-EDTA for protein Tris-acetate-EDTA & Tris-borate-EDTA (50mmol/L; pH 7.5-7.8)
- 5. HEMOGLOBIN ELECTROPHORESIS It is a blood test that can detect different types of hemoglobin. It uses the principles of cellulose acetate & gel electrophoresis to separate out the various types of hemoglobin. The electrophoresis process takes advantage of the fact that hemoglobin types have different electrical charges. During electrophoresis, an electrical current is passed through the hemoglobin in a blood sample, which causes the hemoglobin types to separate at different rates and form bands By comparing the pattern formed with that of a normal blood sample, doctors can see the types and quantities of hemoglobin present in the blood sample
- 6. The test can detect abnormal levels of HbS, the form associated with sickle-cell disease, as well as other abnormal hemoglobin-related blood disorders, such as hemoglobin C. It can also be used to determine whether there is a deficiency of any normal form of hemoglobin, as in the group of diseases known as thalassemias. The hemoglobin electrophoresis is also known to be thalessemia screening, this also can be helpful for the patient who is frequently need of fresh blood transfusion. The patient needs blood transfusion because the body is unable to produce enough hemoglobin to satisfy the body's requirement Hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein inside red blood cells, comes in many molecular forms, some normal and some abnormal. Normal hemoglobin carries and releases oxygen efficiently, while abnormal hemoglobin doesn't.
- 7. THE TYPES OF HAEMOGLOBIN Hemoglobin F: This type is found in growing fetuses and newborns. Soon after birth, it is replaced with hemoglobin A. Hemoglobin A: This is the most common type of hemoglobin found in healthy children and adults. Hemoglobin C, D, E, M, and S: These (and many other, rarer variations) are types of abnormal hemoglobin. If a person inherits the genes that cause production of too much of an abnormal type of hemoglobin, or not enough normal hemoglobin, it can lead to blood disorders due to inherited haemoglobin abnormalities.
- 8. NORMAL VALUES IN ADULTS: Hgb A1: 95% to 98% Hgb A2: 2% to 3% Hgb F: 0.8% to 2% Hgb S: 0% Hgb C: 0% IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN: Hgb F (newborn): 50% to 80% Hgb F (6 months): 8% Hgb F (over 6 months): 1% to 2%
- 9. THERE ARE 3 MAIN CATEGORIES OF INHERITED HAEMOGLOBIN ABNORMALITIES: 1) Structural or qualitative:The amino acid sequence is altered because of incorrect DNA code(Hemoglobinopathy) 2) Quantitative: Produdction of one or more globin chain is reduced or absent(Thalassemia) 3) Hereditary persistence of Fetal haemoglobin(HPFH).complete or partial failure of γ globin to switch to β globin PATHOLOGICAL VARIANTS • Hemoglobin H(β4)-A variant form of Hb formed by a tetramer of β chains which may be present in variants of α thalassemia. • Hemoglobin Barts (γ4)-A variant form of Hb formed by a tetramer of γ chains which may be present in variants of α thalassemia.
- 10. • Hemoglobin S (α2βS2)-A variant form of Hb found in people with sickle cell disease .In the 6th position of globin chain glutamic acid is substituted by valine. Under low oxygen conditions, absence of a polar amino acid in the β chain promotes polymerisation of Hb,which distorts RBC to sickle shape and decrease their elasticity.Sickle cells block the flow of blood in narrow capillaries.Interruption in oxygen supply leads to localised anoxia in the tissues causing cell death. • Hemoglobin C (α2βC2) – Another variant due to variation in the β chain gene. In the 6th position of globin chain glutamic acid is substituted by lysine.This variant causes mild chronic haemolytic anemia. HbC is slower moving than HbA on electrophoresis at alkaline PH.
- 11. • Hemoglobin E (α2βE2) - Another variant due to variation in the β chain gene.This variant causes mild chronic haemolytic anemia. • Hemoglobin AS – A heterozygous form causing sickle cell trait with one adult gene and one sickle cell disease gene. • Hemoglobin SC disease – A compound heterozygous form with one sickle gene and another encoding Hemoglobin C • Hemoglobin D – Also called as HbD Punjab. Results from replacement of beta 121 glutamic acid by glutamine. HbD migrates similar to HbS on electrophoresis at alkaline PH
- 12. LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS TO DETECT ABNORMAL HEMOGLOBIN I ) Red cell morphology HbS – sicke cells HBC – Target cells ,crystals after splenectomy Thalassemias – Microcytosis,Target cells,Basophilic stipplings
- 13. II ) Hemoglobin Electrophoresis Cellulose Acetate At Alkaline pH Citrate Agar Electrophoresis at Acid pH III) Iso electric focusing A pH gradient is established by carrier ampholytes submitted to an electric current and the Hb molecules migrate across this gradient until they reach the position where their net charge is zero (isoelectric point). The molecules will then concentrate in a sharp band IV) High Performance Liquid Chromatography Weak cation exchange column is used.The ionic strength of eluting solution is gradually increased and causes the various Hb variants to have a particular retension time.
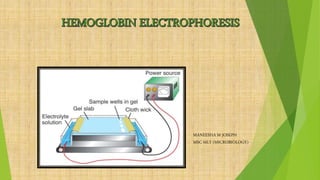
- 14. PRINCIPLE OF CELLULOSE ACETATE ELECTROPHORESIS In an alkaline pH (8.2-8.6) Hb is a negatively charged molecule and will migrate towards the anode (+). The various Hbs moves at different rates depending on their net negative charge, which in turn is controlled by the composition (amino acids) of the Hb molecule (globin chain). The red cell hemolysate (red blood cell membranes are destroyed to free the Hb molecules for testing) is placed in a cellulose acetate membrane, which is positioned in an electrophoresis tray with the inoculated hemolysate near the cathode (-). One end of the cellulose acetate strip is immersed in the buffer (pH 8.2-8.6) on the cathode side and the other end is placed in the buffer on the anode (+) side. An electric current of specific voltage is allowed to run for a timed period. During electrophoresis, the Hb molecules migrate toward the anode because of their negative charge. The difference in the net charge of the Hb molecule determines its mobility and manifests its self by the speed with which it migrates to the positive pole.
- 15. The cellulose acetate membrane is then stained in order to color the proteins (Hbs). By noting the distance each Hb has migrated and comparing this distance with the migration distance of known controls, the types of hemoglobins may be identified. Example of the fast Hbs are Hb Bart’s and the tow fastest variants Hb H and I, while Hb C is the slowest common Hb.
- 16. REQUIREMENTS Haemolysate (a haemolysate is the contents of the red cells) Hemolysate are prepared by addition of water and toluene to saline washed erythrocytes Tris-EDTA Boric Acid (TEB) buffer, pH 8.4. Whatman No. 3 chromatography paper. Cellulose acetate membranes HbA2 control, as supplied by the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control NIBSC. The control has been produced by freeze drying a solution of haemoglobin prepared from human cells and made stable by the addition of sucrose (200 mM), potassium cyanide (6mM) and chloramphenicol (1 mg/dl). This control was established by the World Health Organization in 1994. Protein stain solution (0.5% Ponceau S in 5% TCA) Destain solution (5% acetic acid)
- 17. PROCEDURE 1.Place TEB electrophoresis buffer (about 500 ml total) into all compartments of the electrophoresis tank. Ensure that the level is the same in all compartments by carefully lifting the tank so that the buffer laps over the end of the separating walls. Wipe any excess liquid from the walls with a tissue. 2.Thoroughly wet 2 pieces of Whatman No. 3 filter paper (20 x 7.5 cm) with buffer solution and place them over the edges of the shoulder pieces with one edge of the paper running parallel with edge of the shoulder and the other immersed in the buffer of the outer compartment. These pads act as buffer wicks between the buffer solution and the cellulose acetate strips which are placed between them. 3.Take one cellulose acetate strip and, with a pencil label at one end. Also mark a faint starting line (origin) lightly across the centre of the strip.
- 18. 4.Moisten the strip as follows. Add some TEB buffer to a shallow dish and carefully float the strip on top so that it is impregnated with buffer from below by capillary action. When the strip is thoroughly wetted (3-4 min), it can then be submerged in the buffer. 5.Remove excess buffer from the strip by blotting lightly on filter paper — do not overdry by pressing too hard. 6.Apply the sample applicator to the surface of hemolysate then transfer the sample to origin line on the strip by gently touching the applicator on to the strip .Similarly transfer the control also to the strip 7.Place the strip between the two shoulder pads of the electrophoresis tank, with the origin in the centre and the end with label towards the anode and carefully pull taut. Press the ends of the strip firmly against the pad to ensure proper contact
- 19. 8.Place the Perspex lid on the tank and connect the red and black terminals of the tank to the +ve and -ve terminals of the power supply. 9.Electrophoresis will be carried out at a constant voltage of 150 V (approx. 0.5 mA/cm strip width) for 60 mins. 10.Remove the strip with forceps and carefully float it on the surface of the Ponceau S staining solution, allowing the stain to impregnate the strip from below. When totally wetted, immerse the strip completely in the stain and leave for 5 mins. Agitate occasionally. 11.To destain, drain off excess stain and rinse in a tray of 5% acetic acid. Change the acetic acid once, agitate for a moment, then finally rinse the strip in tap water.
- 23. INTERPRETATION Control in Alkaline electrophoresis: H A F S A2 Sickle Trait This is a heterozygous state showing HbA and HbS and a normal amount of HbA2 on cellulose acetate. Results on citrate agar show hemoglobins in the HbA and HbS migratory positions (zones). Sickle Cell Anemia This is a homozygous state showing almost exclusively HbS, although a small amount of HbF may also be present Sickle-C Disease This is a heterozygous state demonstrating HbS and HbC. Thalassaemia Major This condition shows HbF, HbA and HbA2.
- 24. Sickle Cell –Thalassaemia Disease: This condition shows HbA, HbF, HbS and HbA2. Hemoglobin-C Disease: Disease This is a homozygous state showing almost exclusively HbC Thalassemia-C Disease: This condition shows HbA, HbF, and HbC
- 25. CITRATE AGAR ELECTROPHORESIS ( ACID PH) Citrate agar separates Hb fractions that migrate together on cellulose acetate agar. All Hb specimens that show an abnormal electrophoretic pattern in alkaline media (cellulose acetate agar) should undergo electrophoresis on an acid citrate agar. Citrate agar electrophoresis at acid pH (6.0 to 6.2) permits separation of the major hemoglobins based on the relative mobilities of variant hemoglobins: Hb C from Hb E and Hb O, as well as Hb S from Hb D and Hb G. However, this electrophoresis will not distinguish Hb E from Hb O, nor Hb D from Hb G. Hemoglobin bands are visualized by staining with amido black and acid violet . The procedure should not be used as a screening procedure because many abnormal Hbs migrate with Hb A.
- 26. Electrophoresis of Hbs on agar at acidic pH is not primarily sensitive to the charge of the mutated residue but to structural modifications of positively charged regions of the Hb molecule interacting with the agaro pectin contained in the gel. This property is of special interest to distinguish Hb S from other variants displaying mobility close to that of Hb S on CAE or IEF. This procedure is the method of choice when examining newborns (cord blood specimens) and infants under 3 months of age for some abnormal Hbs such as S and C because the test is able to detect quantities of Hb not easily seen by other techniques
- 27. Citrate agar electrophoresis is carried out on plates of the Helena type. Agar 1gm is suspended in 100 ml of citrate buffer and heated to boiling. Plates were poured by pipetting 10 ml of the hot agar into plastic trays (3 x 3.75 inches) and allowing the agar to gel. Plates are stored at 4 C prior to use. Hemolysate (patient sample & control) is applied on to the gel.The hemolysate reagent contains 0.005 M EDTA in deionized water with 0.07% potassium cyanide added as a preservative. Citrate agar runs are done at room temperature using approximately 40 ma/plate. Plates are run for 45 minutes followed by staining, using o-dianisidine and hydrogen peroxide. Stained plates are washed with 5% acetic acid and dried on cards for storage and photography PROCEDURE
- 28. APPARATUS
- 29. C S A F D G A2 E O CITRATE AGAR ELECTROPHORESIS PATTERN
- 32. WHEN IT IS DONE? A doctor may order hemoglobin electrophoresis to help diagnose diseases (called hemoglobinopathies) involving abnormal hemoglobin production, such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia. Doctors also may order the test when a child has family history of a hemoglobinopathy or is found to have anemia that isn't due to a more common cause, such as iron deficiency. In many states, a hemoglobin electrophoresis is performed as part of a series of newborn screening blood tests, primarily so that kids with sickle cell anemia can be diagnosed, monitored, and treated early to prevent potentially life- threatening complications.
