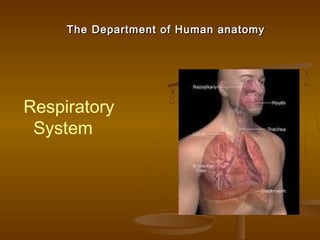
Respiratory system
- 1. The Department of Human anatomyThe Department of Human anatomy Respiratory System
- 2. The The respiratory systemrespiratory system is the anatomical is the anatomical system of an organism that introducessystem of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior andrespiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans theperforms gas exchange. In humans the respiratory system include airways, lungs, andrespiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratorythe respiratory muscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbonmuscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion,dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment andbetween the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in thethe blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungsalveolar region of the lungs
- 3. General Functions of Respiratory System: 1. O2 (oxygen)oxygen) and CO2 (carbon dioxidecarbon dioxide) exchange between blood and air 2. speech and vocalization 3. sense of smell 4. helps control acid base balance of body 5. breathing movements help promote blood and lymph flow
- 4. Main Organs: nose pharynx larynx trachea primary bronchi lungs: bronchioles alveoli/respiratory membrane these organs can also be subdivided into: upper respiratory tract Nose-pharynx-larynx lower respiratory tract respiratory organs of the thorax
- 5. SponsoredSponsored Medical Lecture Notes –Medical Lecture Notes – All SubjectsAll Subjects USMLE Exam (America) –USMLE Exam (America) – PracticePractice
- 6. Functional classifications:Functional classifications: ConductingConducting portion: transports air.portion: transports air. RespiratoryRespiratory portion: carries out gas exchange.portion: carries out gas exchange. respiratory bronchiolesrespiratory bronchioles alveolar ductsalveolar ducts air sacs called alveoliair sacs called alveoli Upper respiratory tract is all conductingUpper respiratory tract is all conducting Lower respiratory tract has bothLower respiratory tract has both conducting and respiratory portionsconducting and respiratory portions
- 7. Air passageways must be held open at all times nasal passageways and throat follow passages in skull bones and cartilage others held open by rings of cartilage
- 8. Nose separated from mouth by hard and soft palate each nasal cavity is divided into 3 passageways by turbinates (choncae) turbulent passageways to insure that all air makes contact with mucous membranes membranes are heavily vascualrized remove bacteria, debris and particles warms and moisturizes air entering lungs also contains receptors for smell nasolacrimal ducts drain into nasal cavity
- 9. Paranasal sinuses:Paranasal sinuses: In four skull bonesIn four skull bones paired air spacespaired air spaces decrease skull bone weightdecrease skull bone weight warm and moisten air sound resonance Named for the bonesNamed for the bones in which they are housed.in which they are housed. frontalfrontal ethmoidalethmoidal sphenoidalsphenoidal maxillarymaxillary Communicate with the nasal cavity by ducts.Communicate with the nasal cavity by ducts. Covered with the same pseudostratified ciliatedCovered with the same pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium as the nasal cavity.columnar epithelium as the nasal cavity.
- 10. Pharynx (throat) - Is situated from base of skull to junction with esophagus and trachea - made of muscle and lined with mucous membrane - junction between digestive and respiratory systems divided into three regions: a. Nasopharynx behind nose to level of soft palate includes uvula, tonsils (adenoids) auditory tube (eustachian tube) b. Oropharynx behind mouth from soft palate to level of hyoid bone palatine and lingual tonsils c. Laryngopharynx from hyoid bone to esophagus/larynx
- 11. Larynx (voice box) enlarged beginning portion of trachea composed of cartilage and muscles opening into larynx = glottis (prevent food from entering lower respiratory system sound) 9 cartilages: three individual piecesthree individual pieces Thyroid cartilageThyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilageCricoid cartilage EpiglottisEpiglottis three cartilage pairsthree cartilage pairs Arytenoids: on cricoidArytenoids: on cricoid Corniculates: attach toCorniculates: attach to arytenoidsarytenoids Cuniforms:in aryepiglottic foldCuniforms:in aryepiglottic fold
- 12. Sound ProductionSound Production Two pairs of ligamentsTwo pairs of ligaments Inferior ligaments, calledInferior ligaments, called vocal ligamentsvocal ligaments covered by a mucous membranecovered by a mucous membrane are “true vocal cords”are “true vocal cords” they produce sound when air passesthey produce sound when air passes between thembetween them Superior ligaments, calledSuperior ligaments, called vestibularvestibular ligamentsligaments Covered by mucosaCovered by mucosa Are “false vocal cords”Are “false vocal cords” no function in soundno function in sound productionproduction protect the vocal folds.protect the vocal folds. The vestibular folds attachThe vestibular folds attach to the corniculate cartilagesto the corniculate cartilages ..
- 13. The tension, length,The tension, length, and position of the vocaland position of the vocal folds determine the quality of the sound.folds determine the quality of the sound. Longer vocal folds produce lower soundsLonger vocal folds produce lower sounds More taunt, higher pitchMore taunt, higher pitch Loudness based on force of airLoudness based on force of air Rima glottidisRima glottidis: opening between the vocal folds: opening between the vocal folds GlottisGlottis: rima glottidis and the vocal folds: rima glottidis and the vocal folds
- 16. Trachea extends from larynx to bronchi (immediately anterior to the esophagus,immediately anterior to the esophagus, inferior to the larynx, superior to theinferior to the larynx, superior to the primary bronchi of the lungsprimary bronchi of the lungs) surrounded by 15 to 2015 to 20 “C” – shaped bands of cartilage ends joined by bands of muscle tissue (holds walls open, prevents collapse) lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- 18. At the level of theAt the level of the sternal anglesternal angle, the, the trachea bifurcates into two smaller tubes,trachea bifurcates into two smaller tubes, called thecalled the right and left primary bronchiright and left primary bronchi.. Each primary bronchus projects laterallyEach primary bronchus projects laterally toward each lung.toward each lung. The most inferior tracheal cartilageThe most inferior tracheal cartilage separates the primary bronchi at theirseparates the primary bronchi at their origin and forms an internal ridge calledorigin and forms an internal ridge called thethe carina.carina.
- 19. Bronchi bronchi resemble trachea in structure (also supported by C-shaped cartilages) also have lots of elastic connective tissue Right primary bronchusRight primary bronchus shorter, wider, and more verticallyshorter, wider, and more vertically oriented than the left primaryoriented than the left primary bronchus.bronchus. Foreign particles are more likely to lodgeForeign particles are more likely to lodge in the right primary bronchus.in the right primary bronchus. each bronchus enters lung and continues to divide into smaller and smaller branches = bronchi, then into microscopic bronchioles because of the extensive branching it formes bronchial tree
- 20. Primary bronchiPrimary bronchi enter the hilum of each lungenter the hilum of each lung Also entering hilum:Also entering hilum: pulmonary vesselspulmonary vessels lymphatic vesselslymphatic vessels nerves.nerves. Secondary bronchi (or lobar bronchi)Secondary bronchi (or lobar bronchi) Branch of primary bronchusBranch of primary bronchus left lung:left lung: two lobestwo lobes two secondary bronchitwo secondary bronchi right lungright lung three lobesthree lobes three secondary bronchi.three secondary bronchi. Tertiary bronchi (or segmental bronchi)Tertiary bronchi (or segmental bronchi) Branch of secondary bronchiBranch of secondary bronchi left lung is supplied by 8 to 10 tertiary bronchi.left lung is supplied by 8 to 10 tertiary bronchi. right lung is supplied by 10 tertiary bronchiright lung is supplied by 10 tertiary bronchi supply a part of the lung called a bronchopulmonarysupply a part of the lung called a bronchopulmonary segment.segment.
- 21. Bronchioles smallest branches of “respiratory tree” <1mm diameter no cartilage rings (but larger branches may have small patches of cartilage) lined with ciliated cuboidal epithelium and layer of smooth muscle asthma affects the smallest terminal bronchioles
- 23. Respiratory Bronchioles, AlveolarRespiratory Bronchioles, Alveolar Ducts, and AlveoliDucts, and Alveoli Contain small saccular outpocketings calledContain small saccular outpocketings called alveoli.alveoli. An alveolus is about 0.25 to 0.5 millimeter inAn alveolus is about 0.25 to 0.5 millimeter in diameter.diameter. Its thin wall is specialized to promote diffusionIts thin wall is specialized to promote diffusion of gases between the alveolus and the blood inof gases between the alveolus and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries.the pulmonary capillaries. Gas exchange can take place in the respiratoryGas exchange can take place in the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts as well as in thebronchioles and alveolar ducts as well as in the lungs, which contain approximately 300–400lungs, which contain approximately 300–400 million alveoli.million alveoli. The spongy natureThe spongy nature of the lung is due to theof the lung is due to the packing of millions of alveoli together.packing of millions of alveoli together.
- 27. Gross Anatomy of the LungsGross Anatomy of the Lungs Each lung has a conical shape.Each lung has a conical shape. Its wide, concave base rests upon the muscular diaphragm.Its wide, concave base rests upon the muscular diaphragm. Its relatively blunt superior region, called the apex orIts relatively blunt superior region, called the apex or (cupola), projects superiorly to a point that is slightly(cupola), projects superiorly to a point that is slightly superior and posterior to the clavicle.superior and posterior to the clavicle. Both lungs are bordered by the thoracic wall anteriorly,Both lungs are bordered by the thoracic wall anteriorly, laterally, and posteriorly, and supported by the rib cage.laterally, and posteriorly, and supported by the rib cage. Toward the midline, the lungs are separated from eachToward the midline, the lungs are separated from each other by the mediastinum.other by the mediastinum. The relatively broad, rounded surface in contact with theThe relatively broad, rounded surface in contact with the thoracic wall is called the costal surface of the lung.thoracic wall is called the costal surface of the lung.
- 33. Pleura and Pleural CavitiesPleura and Pleural Cavities The outer surface of each lung and the adjacentThe outer surface of each lung and the adjacent internal thoracic wall are lined by a serousinternal thoracic wall are lined by a serous membrane called pleura, which is formed frommembrane called pleura, which is formed from simple squamous epithelium.simple squamous epithelium. The outer surface of each lung is tightlyThe outer surface of each lung is tightly covered by the visceral pleura, while thecovered by the visceral pleura, while the internal thoracic walls, the lateral surfaces ofinternal thoracic walls, the lateral surfaces of the mediastinum, and the superior surface ofthe mediastinum, and the superior surface of the diaphragm are lined by the parietal pleura.the diaphragm are lined by the parietal pleura. The parietal and visceral pleural layers areThe parietal and visceral pleural layers are continuous at the hilum of each lung.continuous at the hilum of each lung.
- 34. Pleura and Pleural CavitiesPleura and Pleural Cavities The potential space between theseThe potential space between these serous membrane layers is a pleuralserous membrane layers is a pleural cavity.cavity. The pleural membranes produce a thin,The pleural membranes produce a thin, serous fluid that circulates in the pleuralserous fluid that circulates in the pleural cavity and acts as a lubricant, ensuringcavity and acts as a lubricant, ensuring minimal friction during breathing.minimal friction during breathing.
- 40. Aging and the RespiratoryAging and the Respiratory SystemSystem BecomesBecomes less efficientless efficient with age due to severalwith age due to several structuralstructural changes.changes. Decrease in elastic connective tissueDecrease in elastic connective tissue in the lungs and the thoracicin the lungs and the thoracic cavity wall.cavity wall. Loss of elasticityLoss of elasticity reducesreduces the amount of gas that can be exchangedthe amount of gas that can be exchanged with each breath and results in awith each breath and results in a decreasedecrease in the ventilation rate.in the ventilation rate. EmphysemaEmphysema may cause a loss of alveoli or their functionalitymay cause a loss of alveoli or their functionality Reduced capacity for gas exchange can cause an older person toReduced capacity for gas exchange can cause an older person to become “short of breath” upon exertion.become “short of breath” upon exertion. Carbon, dust, and pollution material graduallyCarbon, dust, and pollution material gradually accumulateaccumulate in ourin our lymph nodes and lungs.lymph nodes and lungs.
- 42. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways,Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type andincluding by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the causepattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause (etiology) of the disease.(etiology) of the disease. Inflammatory lung diseaseInflammatory lung disease Characterised by a high neutrophil count, e.g. asthma, cysticCharacterised by a high neutrophil count, e.g. asthma, cystic fibrosis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonaryfibrosis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder or acute respiratory distress syndrome.disorder or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Allergic reactions due to exposure to certain agents (i.e. foods)Allergic reactions due to exposure to certain agents (i.e. foods) are a relatively common cause of acute respiratory disease.are a relatively common cause of acute respiratory disease. Some common examples include sea foods prawns, someSome common examples include sea foods prawns, some fatty fish, radish, arrow root, lady's finger, lemon, moongfatty fish, radish, arrow root, lady's finger, lemon, moong dhal, peanuts, water content spinach, curd, bananas,dhal, peanuts, water content spinach, curd, bananas, grapes, pomegranates, berries, custard apple, ice creams,grapes, pomegranates, berries, custard apple, ice creams, etc. In summer, bad weather condition mean sandy andetc. In summer, bad weather condition mean sandy and dusty weather or some may affect in winter also.dusty weather or some may affect in winter also.
- 43. Obstructive lung diseasesObstructive lung diseases Obstructive lung diseases are diseases of the lungObstructive lung diseases are diseases of the lung where the airways (i.e. bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli)where the airways (i.e. bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli) become reduced in volume or have free flow of gasbecome reduced in volume or have free flow of gas impeded, making it more difficult to move air in and outimpeded, making it more difficult to move air in and out of the lung.of the lung. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD),Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), which includes asthma an example of an obstructivewhich includes asthma an example of an obstructive lung disease, is where the airways become damaged,lung disease, is where the airways become damaged, causing them to narrow.causing them to narrow.
- 44. AsthmaAsthma Asthma is another example of an obstructive lung disease, (and of anAsthma is another example of an obstructive lung disease, (and of an inflammatory lung disease).inflammatory lung disease). Asthma attacks can be brought on by triggers, such as air pollution,Asthma attacks can be brought on by triggers, such as air pollution, tobacco smoke, factory fumes, cleaning solvents, infections, pollens,tobacco smoke, factory fumes, cleaning solvents, infections, pollens, foods, cold air, exercise, chemicals and medications. Triggers are highlyfoods, cold air, exercise, chemicals and medications. Triggers are highly individual and may not be related to allergens. Many asthmatics are notindividual and may not be related to allergens. Many asthmatics are not allergic to common allergens such as mold, ragweed, dust or pollens.allergic to common allergens such as mold, ragweed, dust or pollens. Restrictive lung diseasesRestrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases (also known as interstitial lung diseases) are aRestrictive lung diseases (also known as interstitial lung diseases) are a category of respiratory disease characterized by a loss of lungcategory of respiratory disease characterized by a loss of lung compliance, causing incomplete lung expansion and increased lungcompliance, causing incomplete lung expansion and increased lung stiffness. E.g. in infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS).stiffness. E.g. in infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS). Respiratory tract infectionsRespiratory tract infections Infections can affect any part of the respiratory system. They areInfections can affect any part of the respiratory system. They are traditionally divided into upper respiratory tract infections and lowertraditionally divided into upper respiratory tract infections and lower respiratory tract infections.respiratory tract infections.
- 45. Upper respiratory tract infectionUpper respiratory tract infection The most common upper respiratory tract infection isThe most common upper respiratory tract infection is the common cold however, infections of specific organs of thethe common cold however, infections of specific organs of the upper respiratory tract such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitisupper respiratory tract such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, pharyngitis and laryngitis are also considered uppermedia, pharyngitis and laryngitis are also considered upper respiratory tract infections.respiratory tract infections. Lower respiratory tract infectionLower respiratory tract infection The most common lower respiratory tract infection inThe most common lower respiratory tract infection in is pneumonia, a lung infection. Pneumonia is usually causedis pneumonia, a lung infection. Pneumonia is usually caused by bacteria, particularlyStreptococcus pneumoniae in Westernby bacteria, particularlyStreptococcus pneumoniae in Western countries. Worldwide, tuberculosis is an important cause ofcountries. Worldwide, tuberculosis is an important cause of pneumonia. Other pathogens such as viruses and fungi canpneumonia. Other pathogens such as viruses and fungi can cause pneumonia for example severe acute respiratorycause pneumonia for example severe acute respiratory syndrome and pneumocystis pneumonia. A pneumonia maysyndrome and pneumocystis pneumonia. A pneumonia may develop complications such as a lung abscess, a round cavitydevelop complications such as a lung abscess, a round cavity in the lung caused by the infection, or may spread toin the lung caused by the infection, or may spread to the pleural cavity.the pleural cavity.
- 46. Respiratory tumorsRespiratory tumors Tumours of the respiratory system are eitherTumours of the respiratory system are either malignant or benign.malignant or benign. Malignant tumorsMalignant tumors Malignant tumors, or cancers of the respiratoryMalignant tumors, or cancers of the respiratory system, particularly lung cancers, are a majorsystem, particularly lung cancers, are a major health problem responsible for 15% of all cancerhealth problem responsible for 15% of all cancer diagnoses and 29% of all cancer deaths.diagnoses and 29% of all cancer deaths.[3][3] The The majority of respiratory system cancers aremajority of respiratory system cancers are attributable to smoking attributable to smoking tobaccotobacco..
